Overview
When using a Entra ID as a single sign on provider for SpiraTest, SpiraTeam or SpiraPlan (aka Spira), you are using the industry-standard protocol OAuth 2.x, also known as OpenID Connect (OIDC).
OpenID Connect is an interoperable authentication protocol based on the OAuth 2.0 framework of specifications (IETF RFC 6749 and 6750). It simplifies the way to verify the identity of users based on the authentication performed by an Authorization Server and to obtain user profile information in an interoperable and REST-like manner.
OpenID Connect enables application and website developers to launch sign-in flows and receive verifiable assertions about users across Web-based, mobile, and JavaScript clients. And the specification suite is extensible to support a range of optional features such as encryption of identity data, discovery of OpenID Providers, and session logout.
How OpenID Connect Works
In general, OIDC uses the following process to securely authorize a user:
- End user navigates to a website or web application (Relying Party or RP) via a browser.
- End user clicks sign-in and is redirected to the login page of the OpenID Provider (OP).
- The user types in their username and password in the OP authentication page.
- The OP authenticates the User and obtains authorization, and sends a one-time authorization code back to the RP.
- The RP receives the authorization code and sends a request to the OP containing the authorization code and the application's client credentials (client key and secret)
- The OP verifies the authorization code, application’s client ID, and application’s client credentials.
- The OP responds with an ID token and access token (and optionally, a refresh token).
- The RP can use the access token to call an API to access information about the user (e.g. their user profile, avatar, etc.)
The following diagram illustrates the key components:
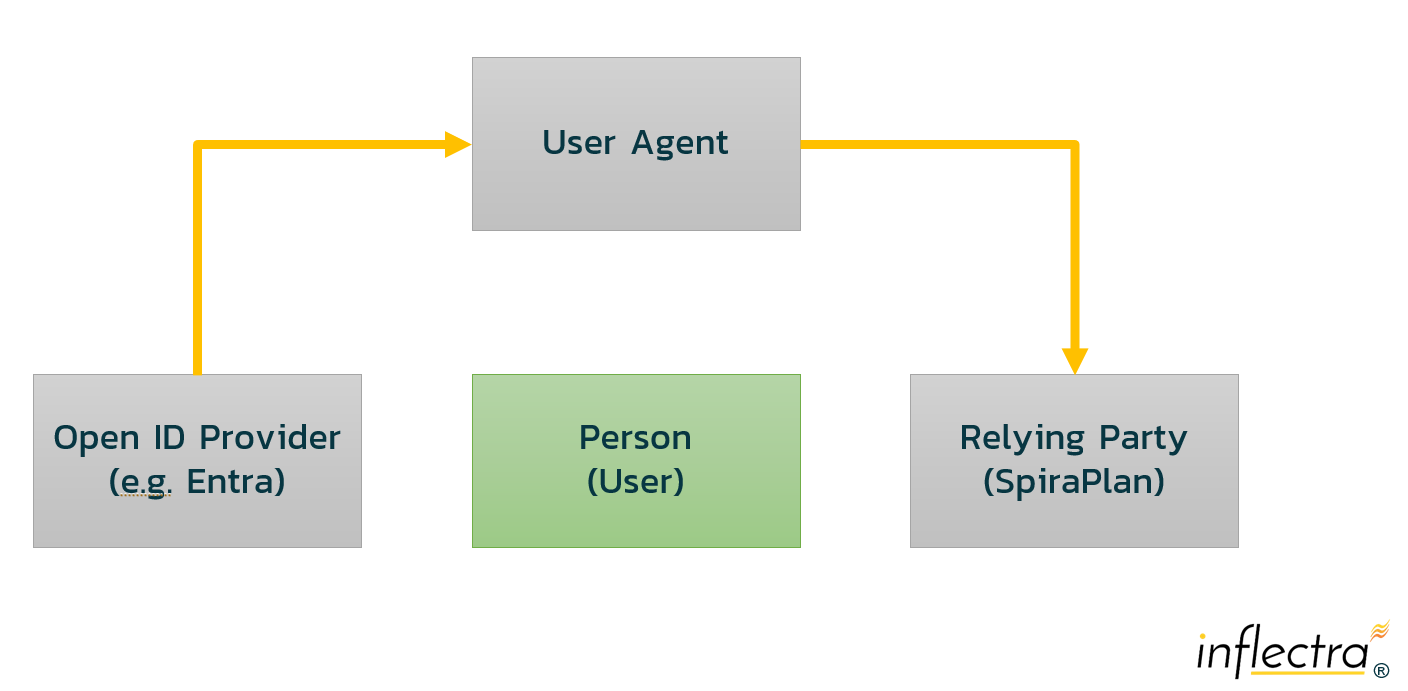
How Spira Connects to Entra
The following architecture diagram illustrates how Spira connects to the various OAuth 2.x (OIDC) providers, including Entra / Azure AD:
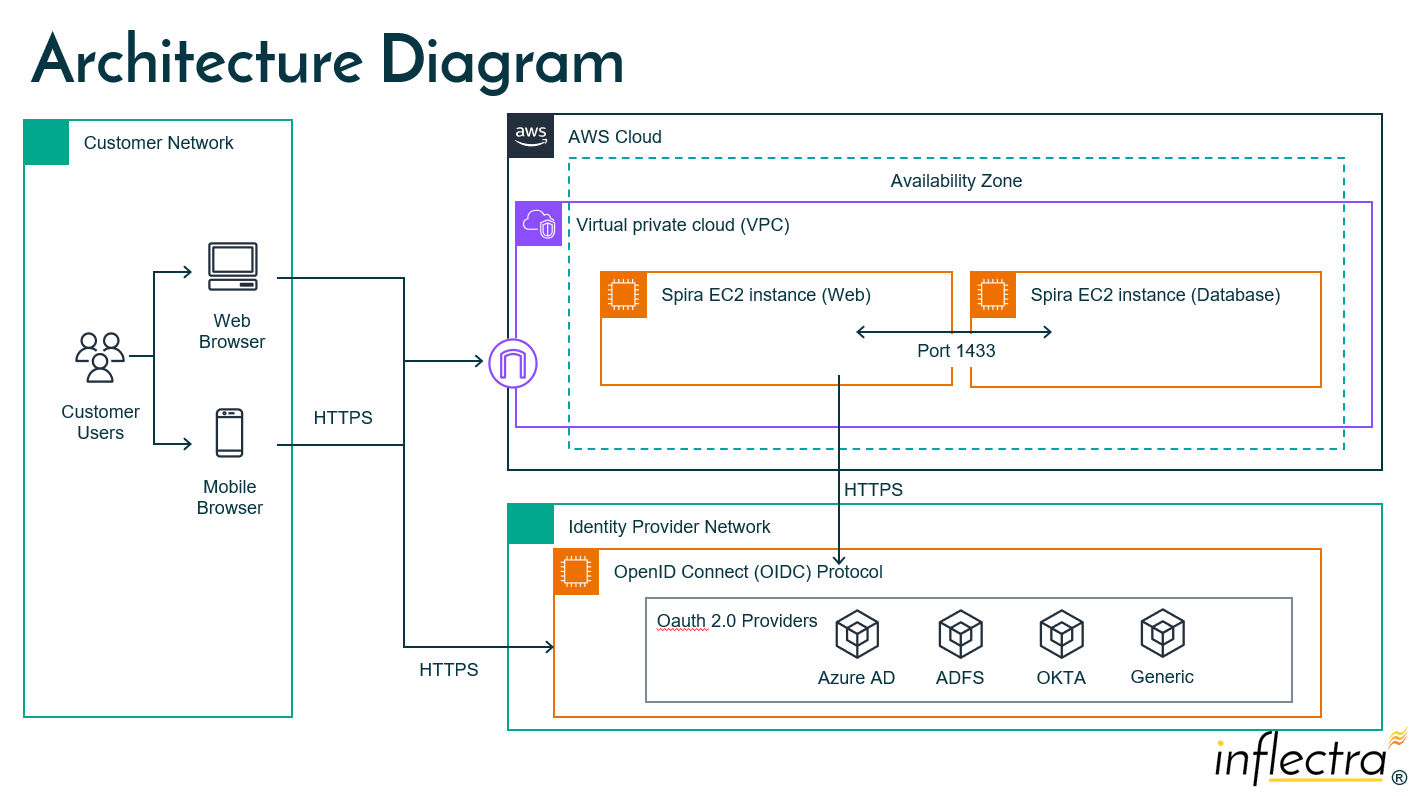
The components in the architecture diagram above are as follows:
- Customer Network is the customer's own network that contains the end users that are going to access Spira, using a web browser.
- AWS Cloud and VPC is the Inflectra AWS account that is used to host and manage the customer's instance of Spira.
- Spira EC2 instance refers to the virtual machines (VMs) running in AWS that hosts Spira's application and database
- Identity Provider Network refers to the network and platform hosting the OIDC identity provider (e.g. AzureAD / Entra, ADFS, OKTA, etc.)
Sequence Diagram
The detailed sequence diagram of a typical user flow is shown below:
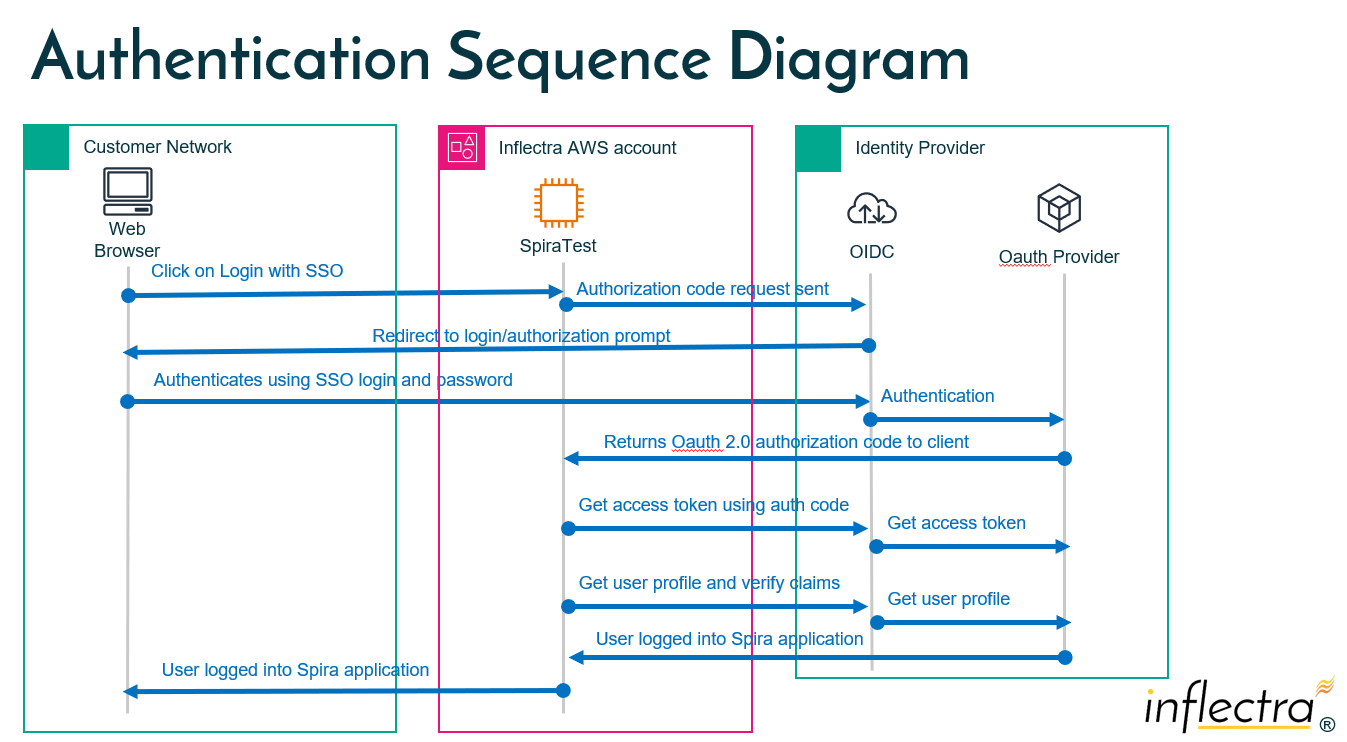
The following steps will occur:
- The user goes to the Spira login page
- The user chooses to authenticate with Entra using the "Azure AD" SSO option
- The user is redirected to the Microsoft Entra login page where they authenticate with a login, password and (if enabled) 2FA token
- If successful, the user is redirected back to Spira, with a special short-lived authorization code
- SpiraPlan takes the authorization code and sends it to Entra
- Entra exchanges the authorization code for an access token
- SpiraPlan receives the access token from Entra
- SpiraPlan uses the access token to get the user profile and verify that the user is allowed to connect to Spira (verifies the claims)
- If the claims are valid, Spira matches the returned user profile to a user profile in its database, and then initiates a valid session.
- The user is now logged into Spira and has an active session.
Authentication Flow for Invalid Entry
While the primary diagram illustrates a successful authentication, it's important to understand the flow when an invalid authentication entry occurs. This scenario primarily involves the interaction between the End-User and Microsoft Entra ID (Identity Provider).
Process Flow: Invalid Authentication Entry
End-User navigates to the SpiraPlan login page and clicks on the "Azure AD" (SSO) option.
SpiraPlan (Client/Relying Party) redirects the End-User's browser to Microsoft Entra ID's authentication endpoint.
End-User is presented with the Microsoft Entra ID login page.
End-User enters invalid credentials (e.g., incorrect username, wrong password, or invalid MFA response).
Microsoft Entra ID (Identity Provider) attempts to verify the credentials.
Microsoft Entra ID (Identity Provider) determines the credentials are invalid.
Microsoft Entra ID (Identity Provider) displays an error message to the End-User (e.g., "Incorrect password," "That Microsoft account doesn't exist," or a similar error indicating authentication failure).
Microsoft Entra ID (Identity Provider) typically does NOT redirect back to SpiraPlan with an authorization code or tokens. Instead, it keeps the user on the login page or redirects to an error page within its own domain.
The End-User must then either correct their credentials and re-attempt login, or choose a different login method.
Key Differences from Successful Flow:
The crucial point is that Microsoft Entra ID acts as the gatekeeper. If the credentials are invalid, it will prevent the issuance of an authorization code or tokens.
SpiraPlan will not receive a valid response from Microsoft Entra ID that would allow it to establish a user session.
The error handling for invalid credentials is primarily managed by Microsoft Entra ID's user interface, informing the user directly about the failure. SpiraPlan only gets involved again if a successful authentication (and subsequent redirection) from Microsoft Entra ID eventually occurs.